Difference Between Active and Passive Exoskeletons
What Are Active and Passive Exoskeletons?
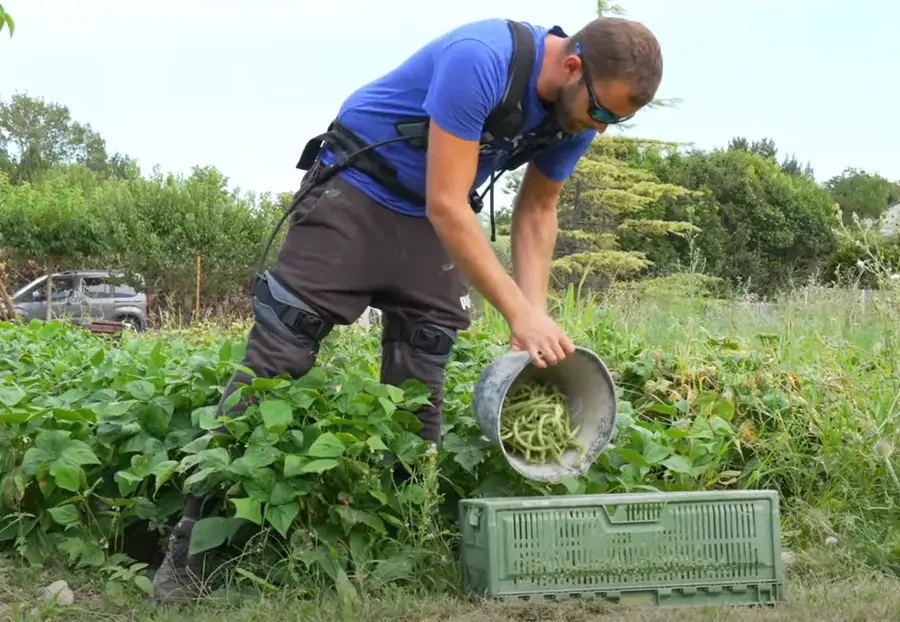
Exoskeletons, as wearable devices designed to assist or enhance human physical performance, can be broadly classified into two types: active and passive. Understanding the difference between active and passive exoskeletons is crucial when selecting the right solution for specific tasks or industries. While both serve the purpose of reducing physical strain and improving efficiency, their methods of operation and intended applications differ significantly.
Active Exoskeletons: Technology-Powered Assistance
Passive Exoskeletons: Simplified Mechanical Support
Key Differences at a Glance
Power Source: Active exoskeletons use motors and batteries, while passive exoskeletons function mechanically.
Cost and Maintenance: Active exoskeletons are costlier and require regular maintenance, whereas passive ones are more affordable and low-maintenance.
Weight: Passive exoskeletons are generally lighter than active exoskeletons.
Applications: Active models are suitable for dynamic tasks like heavy lifting or rehabilitation, while passive ones are best for repetitive or static tasks.
Which Type Should You Choose?
Related Posts
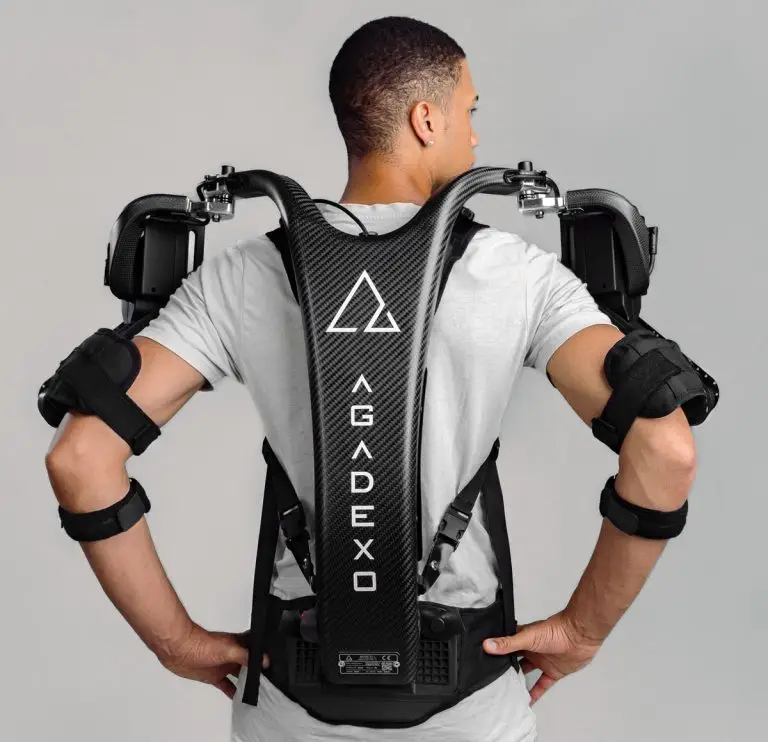

How the Agadexo Exoskeleton Redefines Workplace Efficiency
The Agadexo Exoskeleton is a game-changer in workplaces like manufacturing, logistics, and assembly lines. Its semi-active design reduces the physical load on the shoulders and upper back by up to 40%, as validated by studies performed under EAWS® certification guidelines. But what sets Agadexo apart?